Properly determining the installation location, operating conditions, and environmental factors for self-aligning roller bearings in mechanical equipment is a prerequisite for selecting the appropriate self-aligning roller bearing. To achieve this, it is necessary to gather data and information in the following areas:
(1) Function and structure of the mechanical device
(2) Application location of the self-aligning roller bearing
(3) Load on the self-aligning roller bearing (size, direction)
(4) Rotational speed
(5) Vibration and impact
(6) Operating temperature (ambient temperature, temperature rise)
(7) Ambient conditions (corrosiveness, cleanliness, lubrication)
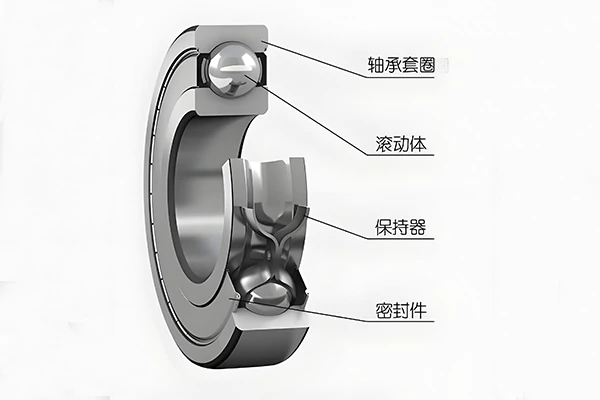
Stiffness of Self-Aligning Roller Bearings
The stiffness of self-aligning roller bearings is determined by their elastic deformation under load. Generally, this deformation is minimal and can be disregarded. However, in certain machinery, such as machine tool spindle systems, the static and dynamic stiffness of self-aligning roller bearings significantly impacts system performance. Spherical roller bearings exhibit higher stiffness than ball bearings. Through appropriate preloading, various bearing types can also enhance their stiffness to varying degrees.
Spherical roller bearings are suitable for heavy loads
Load magnitude is typically the determining factor in bearing size selection. For identical external dimensions, roller bearings offer higher load capacity than ball bearings. Ball bearings are generally suitable for light to medium loads, while roller bearings are designed for heavy loads.
For pure radial loads, deep groove ball bearings or cylindrical roller bearings may be used. For pure axial loads, thrust ball bearings and thrust cylindrical roller bearings can be used. When both radial and axial loads (combined loads) are present, angular contact ball bearings or tapered roller bearings are typically selected. If the radial load is large and the axial load is small, deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings with ribs on both inner and outer rings can be used. If significant shaft or housing deformation and misalignment persist, self-aligning ball bearings or self-aligning roller bearings may be selected. For applications with high axial loads and low radial loads, thrust angular contact ball bearings are suitable. If self-aligning capability is also required for four-point contact ball bearings, thrust self-aligning roller bearings can be chosen.
Corrosion and Damage of Clutch Release Bearings: Symptoms and Common Causes
Clutch Release Bearing Burnout Symptoms: Similar t…
Operating and Environmental Conditions for Spherical Roller Bearings
Properly determining the installation location, op…
Miniature Bearings — Four Core Application Areas
Miniature bearings are suitable for various indust…
Failure Analysis of Engine Crankshaft Rolling Bearings
The crankshafts of some small wheeled tractors are…
Methods for Removing Bearing Inner and Outer Rings
It is well known that regular maintenance is essen…
Six Steps to Prevent Bearing Failures in Industrial Production
High-performance industrial bearings are critical …