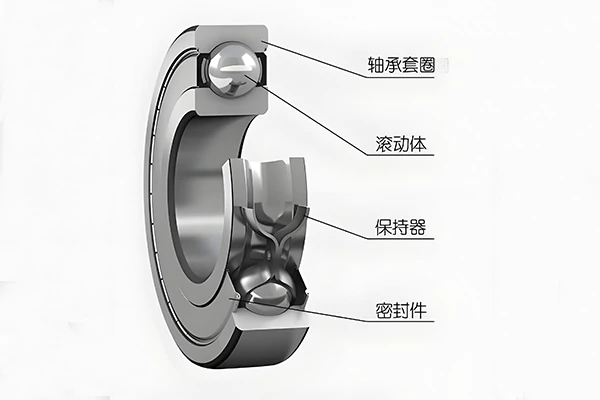
High-performance industrial bearings are critical to ensuring continuous production processes. As the core connectors between processes, bearings bear the weight of machinery and production loads, serving as unsung heroes—until years of wear and tear overwhelm them, forcing recognition of their importance and necessitating shutdowns for professional maintenance.
If bearings operate abnormally, the equipment spindle may face the risk of failure and damage. We can implement a series of measures to prevent abnormal bearing wear, extend their service life, thereby enhancing process availability and environmental safety. Simultaneously, multiple indicators can help detect potential bearing failures early.
Regardless of whether your equipment has recently experienced bearing failures, it remains undeniable that bearings undergo continuous wear with every process cycle. The following six core measures can effectively prevent production issues caused by bearings:
1. Selecting a Suitable Bearing Design Solution
Selecting bearings based on parameters specified in original equipment manufacturer (OEM) documentation is fundamental to ensuring proper operation. Bearings must be capable of withstanding actual working loads—for example, conveyor belt drives and direct-drive equipment have significantly different bearing performance requirements.
Additionally, selecting the correct bearing size is critical to prevent premature wear or failure. Always consult the equipment manufacturer's recommendations: unless a redesign is required due to equipment failure, prioritize OEM-matched models when replacing bearings.
II. Proper Bearing Storage
Today, most factories minimize spare parts inventory by implementing predictive or preventive maintenance to identify potential failures early. This allows for corrective actions, ordering, and bearing replacement before downtime occurs—
purchasing components only when needed, eliminating the need for long-term stockpiling of equipment spares and bearings.
However, in certain situations, bearings and equipment containing bearings must remain stored within factory workshops. Even when stored on shelves, bearings in such environments can be affected by vibrations generated by surrounding operational equipment. Therefore, bearings require standardized storage practices: implement regular rotational maintenance. Prolonged non-rotation causes vibration-induced surface indentations on bearing rings, ultimately leading to premature failure.
III. Proper Bearing Installation
Forcibly installing bearings is strictly prohibited. Heating is recommended to simplify the installation process. For rolling bearings, for example, the inner ring will tightly adhere to the shaft upon cooling after installation. Preheating the inner ring reduces installation difficulty and ensures fitting accuracy.
After completing installation according to the manufacturer's instructions, flush and clean the bearings with lubricant. Finally, apply an appropriate amount of lubricant before equipment startup—lubrication is a key measure for extending bearing service life.
IV. Lubricate Bearings According to Original Specifications
Proper lubrication significantly extends bearing and equipment lifespan: Insufficient lubrication intensifies metal-to-metal friction between balls, cages, and raceways, causing severe wear. Excessive lubrication impedes heat dissipation, leading to wax buildup that causes bearing sticking and restricted movement. Both scenarios ultimately reduce equipment efficiency and production output.
Proper lubrication requires adherence to these principles: Use lubricants with appropriate viscosity matching load requirements (specific parameters determined by equipment manufacturers), avoid exceeding lubricant temperature limits, and strictly prevent contamination by dirt or other impurities.
Manufacturers can assess lubrication status by monitoring stress waves generated by friction. Certain industrial inspection tools capture short-circuit signals and high-frequency stress waves, generating corresponding charts. The chart on the right illustrates the condition of a faulty bearing: seal leakage caused lubricant loss. Under insufficient lubrication, the software-generated chart clearly shows impact signals—these signals appear randomly, with some peaks reaching 32 G-seconds, and suddenly reaching high alarm fault levels, directly indicating insufficient lubrication.
Improper lubrication may cause bearings' rollers to shift and rebound against inner or outer rings, generating stress waves. New technologies enable frequency analysis and stress wave monitoring to detect and resolve bearing anomalies early. Factories can also employ ultrasonic testing to assess bearing condition and determine optimal lubricant quantities, reducing friction losses.
V. Precision Alignment Installation
In production environments, the core responsibility of maintenance teams is to repair equipment and restore production quickly. Precision alignment is essential to fulfilling this task. Correct shaft alignment enhances the reliability and availability of production equipment, extending its service life by months or even years in certain scenarios.
If connecting components are not precisely aligned, abnormal wear will occur in the bearings of equipment or units. Flexible mechanical couplings can absorb a certain degree of misalignment, but this characteristic does not apply to mechanical bearings—misalignment will cause premature bearing wear. Simultaneously, misaligned units will also experience issues such as high energy consumption and low efficiency.
Best practice: Proactively perform alignment checks before commissioning equipment or units to eliminate misalignment risks prior to startup. Record pre-operation alignment data to enable maintenance teams to compare daily operating parameters against baseline values for analysis. Laser alignment systems ensure precise installation of connected components before recommissioning.
VI. Ensure Equipment Dynamic Balancing
Equipment imbalance (e.g., fan imbalance) subjects bearings to additional loads, shortening their service life. Vibration diagnostic equipment or professional vibration analysts can detect imbalance issues. Collected data helps determine whether precise balancing or thorough cleaning to remove buildup is required. During maintenance, ensure components are precisely repositioned and correctly reassembled (mark all parts before disassembly). Re-test for imbalance after maintenance or repairs.
Monitoring trend data helps analysts develop corrective actions for imbalance issues: Over time, normal wear and material buildup cause imbalance to increase slowly and steadily. If a component fails or is incorrectly assembled, the imbalance trend will suddenly worsen. Regardless of the cause, the additional stress on bearings leads to abnormal wear and premature failure.
Additional Diagnostic Methods
If bearings still require replacement every few months despite strict adherence to the above six measures, conduct a root cause failure analysis (RCFA). For instance, if abnormal wear marks persist on rolling bearings, contact the bearing manufacturer for inspection to verify whether lubrication adequately supports the operating load.
Vibration analysis is a non-destructive, non-invasive inspection method that precisely identifies bearing wear levels, installation errors, and other mechanical issues. It provides deep insight into the internal condition of equipment, enabling selection of appropriate solutions for problems identified in comprehensive vibration analysis.
Infrared thermal imaging technology monitors coupling and bearing temperatures, assisting in determining whether failures are temperature-related (e.g., overheating or insufficient cooling).
Oil analysis examines lubricant or oil samples to detect abnormal wear particles or contaminants within bearings. This method is also effective for identifying internal contact issues in sliding bearings—confirmed by analyzing Babbitt alloy composition in the sample.
Whether conducted by internal teams or third-party experts, bearing analysis is a critical component of factory installation and maintenance procedures, significantly impacting both short-term and long-term investment returns.
Corrosion and Damage of Clutch Release Bearings: Symptoms and Common Causes
Clutch Release Bearing Burnout Symptoms: Similar t…
Operating and Environmental Conditions for Spherical Roller Bearings
Properly determining the installation location, op…
Miniature Bearings — Four Core Application Areas
Miniature bearings are suitable for various indust…
Failure Analysis of Engine Crankshaft Rolling Bearings
The crankshafts of some small wheeled tractors are…
Methods for Removing Bearing Inner and Outer Rings
It is well known that regular maintenance is essen…
Six Steps to Prevent Bearing Failures in Industrial Production
High-performance industrial bearings are critical …