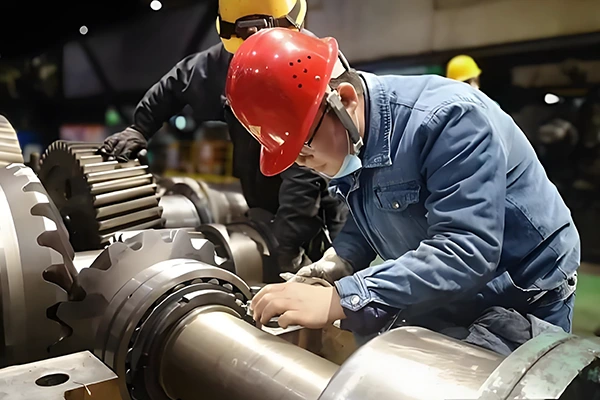
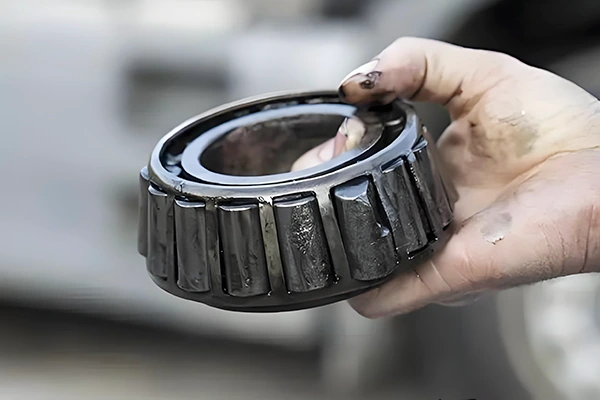
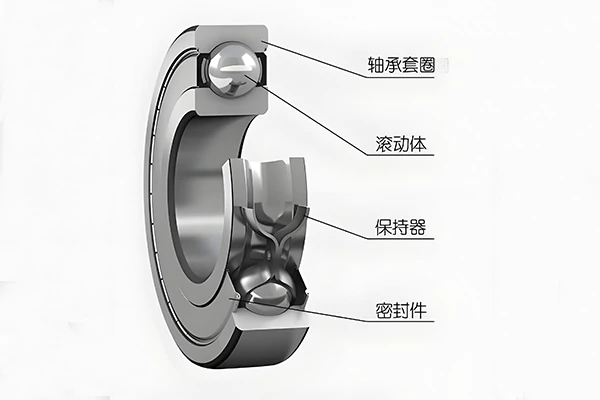
To preserve the original performance of rolling bearings and ensure their stable operation under long-term favorable conditions, regular inspection and maintenance are required. This prevents failures, safeguards equipment reliability, and ultimately enhances operational efficiency and overall benefits.
Routine maintenance must be performed according to the operating conditions and standard specifications of the machinery. Core activities include monitoring equipment operating status, replenishing or replacing lubricants, and conducting periodic disassembly inspections.
Maintenance items during operation cover key indicators such as bearing operating noise, vibration amplitude, operating temperature, and lubricant condition.
Abnormalities during operation must be identified in real time, root causes investigated, and corresponding corrective actions taken. When necessary, meticulously inspect bearings after disassembly.
Bearing Abnormality Detector
Predicting abnormal conditions during bearing operation is a critical aspect of the production process. Bearing abnormality detectors monitor bearing status in real time. Upon detecting anomalies, they immediately trigger alarm signals or initiate automatic shutdown procedures, effectively preventing fault escalation and enabling scientific maintenance.
Bearing Failure Modes and Countermeasures
Under proper usage, bearings typically achieve their expected fatigue life. However, unexpected premature failure renders them unusable. Such failure unrelated to fatigue life is termed failure or catastrophic damage, often caused by inadequate installation, usage, or lubrication practices; foreign object intrusion; or insufficient design consideration for shafts and bearing housings.
Bearing damage conditions (e.g., scratches on roller bearing rings or flanges) may result from one or multiple causes: insufficient lubrication or improper lubricant selection, defects in oil supply/drainage structures, foreign object intrusion, bearing installation misalignment, or excessive shaft deflection.
Therefore, identifying the root cause solely through damage inspection is challenging. However, by thoroughly understanding the equipment, operating conditions, and surrounding structures where the bearing is installed, clarifying the specific circumstances before and after the failure, and conducting a comprehensive analysis combining bearing damage characteristics with various related factors, it is possible to effectively prevent similar failures from recurring. Below are typical causes of bearing damage and corresponding countermeasures.
Bearing Maintenance and Repair
To preserve the original performance of rolling be…
Installation Methods for Different Types of Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are a type of rolling beari…
Causes of Bearing Overheating and Troubleshooting
In the daily operation of industrial equipment, ab…
Material Selection Analysis for Wind Turbine Main Shaft Bearings
In wind power equipment, the main shaft bearing is…
What materials are used for automotive bearings?
In wind power equipment, the main shaft bearing is…
What are the commonly used materials for motor bearings?
The primary materials commonly used for motor bear…