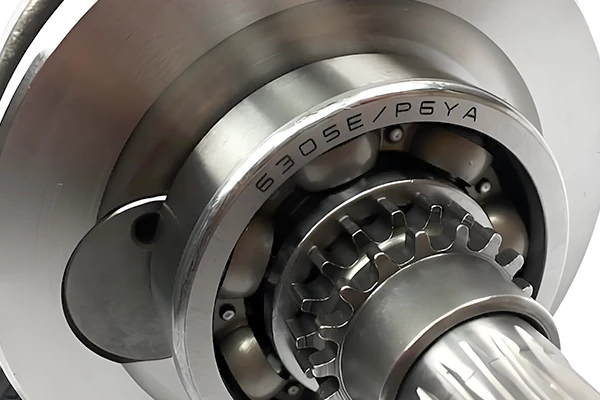
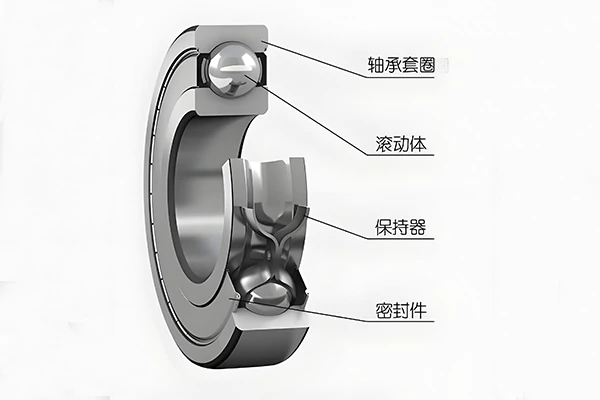
The clearance of a rolling bearing refers to the maximum radial or axial movement of one ring when the other ring is fixed. It is divided into two types: radial clearance and axial clearance. When assembling rolling bearings, the clearance should not be too large or too small. Excessive clearance reduces the number of rolling elements capable of simultaneously bearing loads, increasing the load on individual rolling elements. This lowers the bearing's rotational precision and shortens its service life.
Insufficient clearance increases friction, leading to heightened heat generation, accelerated wear, and also shortened bearing life. Therefore, clearance must be strictly controlled and adjusted during bearing assembly. Preload refers to applying axial force to the inner or outer ring during assembly to eliminate clearance and induce initial deformation at the contact points between the rolling elements and the inner/outer ring. Preload enhances bearing stiffness and rotational accuracy under operating conditions. Bearings subjected to heavy loads and requiring high rotational precision typically operate with zero clearance or slight interference, necessitating preload adjustment during assembly. Clearance adjustment and preload are usually achieved through appropriate axial relative displacement between the inner and outer rings.
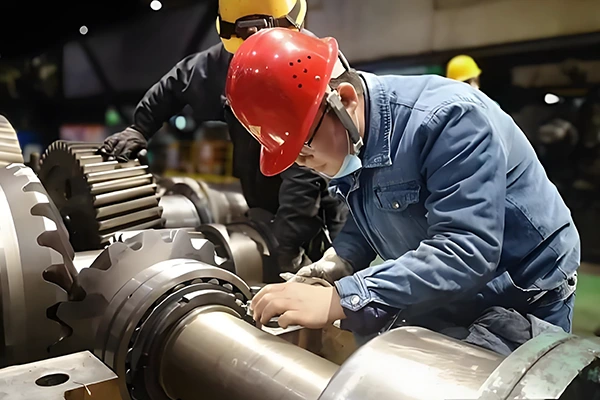
Before installing bearings, thoroughly clean the bearing, shaft journal, and bearing housing bore. During installation, use specialized tools to press the bearing evenly, avoiding direct impact with hard objects like hammers. If specialized tools are unavailable, use a copper rod or wooden block as a cushion before hammering to ensure even pressure distribution across the inner and outer rings. This prevents one-sided pressure, bearing tilt, mating surface damage, or installation eccentricity.
During installation, if excessive tightness or looseness is detected between the bearing journal and housing bore, halt installation and select a suitable bearing for reinstallation. Any misalignment in the journal or housing bore must be corrected before proceeding.
After installation, start the machine to measure bearing housing temperature and listen for abnormal sounds. Excessive temperature indicates insufficient clearance; unusual noises may signal excessive play. Adjust the clearance after stopping the machine based on inspection results.
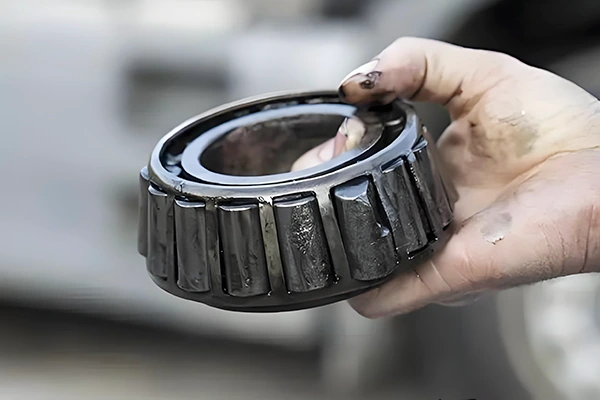
When disassembling bearings, take special care not to transmit pressure through the rolling elements to avoid damaging the bearing cage. Use a puller to slowly remove the bearing whenever possible. If a puller is unavailable, gently tap the bearing with a copper rod or wooden block as a spacer, taking care not to damage the shaft journal or bearing housing bore surface.
Bearing Maintenance and Repair
To preserve the original performance of rolling be…
Installation Methods for Different Types of Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are a type of rolling beari…
Causes of Bearing Overheating and Troubleshooting
In the daily operation of industrial equipment, ab…
Material Selection Analysis for Wind Turbine Main Shaft Bearings
In wind power equipment, the main shaft bearing is…
What materials are used for automotive bearings?
In wind power equipment, the main shaft bearing is…
What are the commonly used materials for motor bearings?
The primary materials commonly used for motor bear…