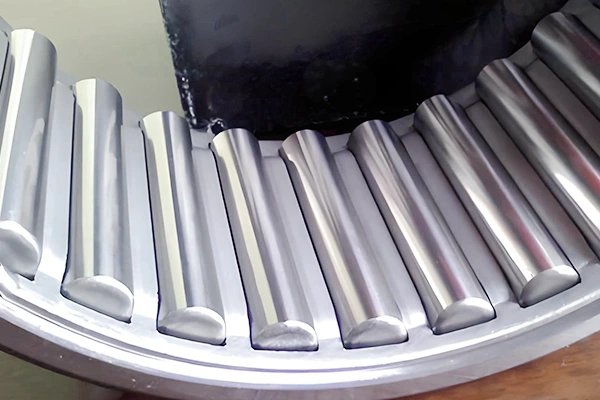
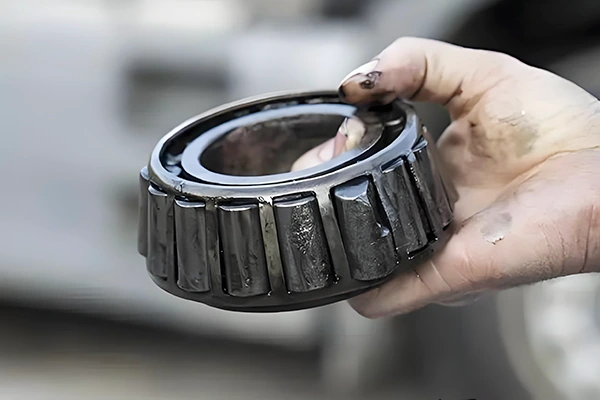
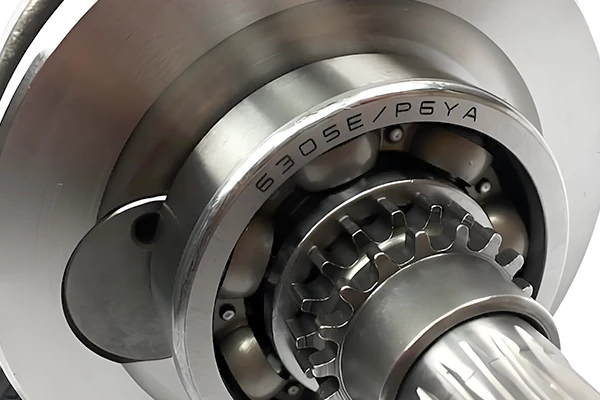
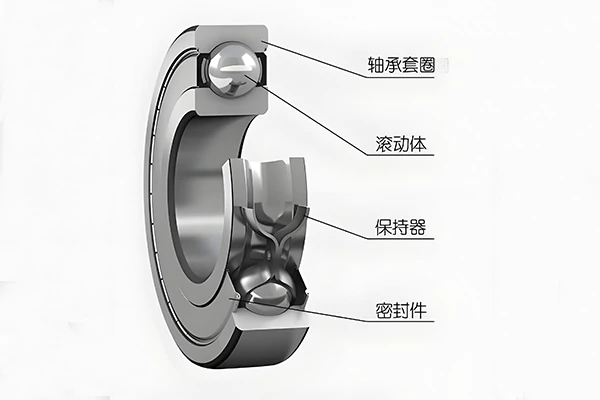
In a significant development for engineering and manufacturing, experts have highlighted the key distinctions between roller bearings and ball bearings—two critical components in machinery. Roller bearings utilize cylindrical rollers to distribute loads across a larger surface area, making them ideal for applications requiring high radial load capacity.
This design offers enhanced stability and durability, particularly in heavy-duty scenarios.
Conversely, ball bearings employ spherical balls to facilitate smooth rotational motion, proving advantageous in applications where speed and low friction are paramount. They excel in environments with lighter loads and higher speeds, such as in electric motors and household appliances.
Industry analysts note that the choice between roller bearings and ball bearings largely depends on the specific requirements of the application. Roller bearings may be preferred for heavy machinery, while ball bearings suit high-speed operations. As technology advances, manufacturers increasingly innovate in materials and design, enhancing the efficiency and performance of both bearing types. This distinction not only informs engineers but also plays a crucial role in the advancement of modern mechanical systems.
Bearing Maintenance and Repair
To preserve the original performance of rolling be…
Installation Methods for Different Types of Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are a type of rolling beari…
Causes of Bearing Overheating and Troubleshooting
In the daily operation of industrial equipment, ab…
Material Selection Analysis for Wind Turbine Main Shaft Bearings
In wind power equipment, the main shaft bearing is…
What materials are used for automotive bearings?
In wind power equipment, the main shaft bearing is…
What are the commonly used materials for motor bearings?
The primary materials commonly used for motor bear…